By Sophie Birkett | Charitable Trust manager
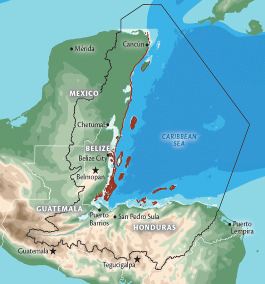
The Mesoamerican barrier reef system (MBRS) extends over four countries, from the tip of the Yucatan peninsula in Mexico down to Belize, Honduras, and Guatemala. It is the second largest barrier reef in the world and the home to over 500 fish species as well as numerous endangered species such as the Loggerhead turtle, Nassau and goliath groupers and black coral. There are an estimated 2 million people directly linked to the MBRS coastal environments, depending on the health of the ecosystem for food, water, livelihoods and income. Its marine and coastal ecosystem provides the foundation for the Yucatan peninsulas multi-billion dollar tourism industry. These activities are continuing to increase in the area, placing varying degrees of pressure on the natural ecosystems of the MBRS.
Due to its importance, a program known as the synoptic monitoring program (SMP) was developed to assess the health of the reef. The MBRS SMP was designed as a standardized methodology to monitor changes in ecosystem health with the aim of improving the management of the coastal and marine resources.The Marine Conservation Expedition run by GVI in collaboration with Amigos de Sian Ka’an, is located in the Sian Ka’an Biosphere Reserve,Tulum, Mexico, in a place called Pez Maya.This programme trains volunteers on the SMP methodology in order to monitor fish, coral, algae and other sessile organisms in the reef .
Following learning a list of target species and the SMP methodology, volunteers are able to monitor within 100m of GPS marked sites. The SMP method Pez Maya uses involves belt transects. It is designed to measure the density and sizes of selected Caribbean key fish species, such as predators, herbivores, and “indicator” species, many of which are commercially exploited. For each transect, volunteers record the following information: recorder’s name, date, time of start of transect, Site name and GPS location, transect number
Links:
Project reports on GlobalGiving are posted directly to globalgiving.org by Project Leaders as they are completed, generally every 3-4 months. To protect the integrity of these documents, GlobalGiving does not alter them; therefore you may find some language or formatting issues.
If you donate to this project or have donated to this project, you can receive an email when this project posts a report. You can also subscribe for reports without donating.
Support this important cause by creating a personalized fundraising page.
Start a Fundraiser